Chapter 11
Policy Change Events
The Policy Change audit category include six subcategories and provides notification of changes to important security policies on the local system, such as to the system’s audit policy or, in the case of DCs, trust relationships.
|
Policy Change Subcategories
|
Comment
|
|
Audit Policy Change
|
Policies that affect what gets reported and misc policies
|
|
Authentication Policy Change
|
Logon rights assignments
|
|
Authorization Policy Change
|
Privilege (rights) assignments
|
|
MPSSVC Rule Level Policy Change
|
Firewall Policy Changes
|
|
Filtering Platform Policy Change
|
Firewall used Windows Filtering Platform; May be used by
others
|
|
Other Policy Change Events
|
One Windows Filtering Platform event
|
Audit Policy Change
|
Event ID
|
Title
|
|
4715
|
The audit policy (SACL) on an object was changed.
|
|
4719
|
System audit policy was changed.
|
|
4902
|
The Per-user audit policy table was created.
|
|
4904
|
An attempt was made to register a security event source.
|
|
4905
|
An attempt was made to unregister a security event source.
|
|
4906
|
The CrashOnAuditFail value has changed.
|
|
4907
|
Auditing settings on object were changed.
|
|
4912
|
Per User Audit Policy was changed.
|
Windows allows applications to report their own security
events to the Security log by registering through Authorization Manager, using Local Security Authority (LSA) as a security event source. The application uses the AuthzRegisterSecurityEventSource function to register. Event IDs 4904 and 4905 indicate that applications have been registered and unregistered.
The event ID 4715 description, The audit policy (SACL) on an object was changed, is poorly worded. The event actually
indicates that the security descriptor on an audit policy was changed,
meaning that the ability to change an audit policy has been delegated or that
such delegation has been removed. (You can use the auditpol /set /sd: command to delegate authority to the system's audit policy.) The event will show the old and new security descriptor in Security Descriptor Definition Language (SDDL) format. See http://msdn2.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa379567.aspx
for more information.
Event ID 4719 is an important event that indicates that
the System audit policy was changed. This event tells you that one of
the 50 policy subcategories was changed and gives you the details. If one of
the nine primary categories is changed, you will see an event for each of the
changed subcategories. An improvement to this event in Windows Server 2008 and later is
that the event now shows both the old and new policy. If the policy was changed
through Group Policy, the Subject will indicate the computer account that
initiated the change. To determine who actually made the change, the applicable
GPO must also be audited. (See chapter 9 for auditing changes to Group Policy.)
Event ID 4906 is logged when you change the value of the
Audit:
Shut down system immediately if unable to log security audits
security
option. This change can be used to make the system crash (i.e., “blue screen”)
if the Security log fills and is configured not to overwrite or autobackup.
Whenever an audit policy is changed on a file or folder object,
event ID 4907 records both the old and the new SACL. Instances of
this event can be quite numerous on a system that is being set up or changed
frequently but will help ensure continuous auditing. The event occurs even when
Object Auditing is not set. The event does not record changes for the SACLs on
DS objects.
Authentication Policy Change
The Authentication Policy Change subcategory events track any configuration changes that would affect how user accounts are
authenticated and when password and lockout policies are conspicuously missing.
|
Event ID
|
Title
|
|
4706
|
A new trust was created to a domain.
|
|
4707
|
A trust to a domain was removed.
|
|
4713
|
Kerberos policy was changed.
|
|
4716
|
Trusted domain information was modified.
|
|
4717
|
System security access was granted to an account.
|
|
4718
|
System security access was removed from an account.
|
|
4865
|
A trusted forest information entry was added.
|
|
4866
|
A trusted forest information entry was removed.
|
|
4867
|
A trusted forest information entry was modified.
|
Trusted Domain Events
When a trust is created, removed, or modified on a domain,
a Policy Change event occurs. The subject fields indicate who made the change.
The other fields require a little translation as you can see in Event ID 4716.
Trusted Domain
Despite the word "Trusted" in the event
description, the other domain in this trust relationship can be a trusting
domain, a trusted domain, or both. (The New Trust Information will provide this
information.) Under the Trusted Domain information, you’ll find the Domain
Name, which states the DNS name of the domain, and the Domain ID, which states
the pre-Windows 2000 (NetBIOS) name of the domain.
New Trust Information
The New Trust Information defines the type of trust after
this change: whether it is one way or mutual, transitivity, and so forth. This
information includes the Trust Type, Trust Direction and Trust Attributes, which are a bitwise value comprising any of the
following:
- TRUST_ATTRIBUTE_NON_TRANSITIVE 1
- TRUST_ATTRIBUTE_UPLEVEL_ONLY 2
- TRUST_ATTRIBUTE_FILTER_SIDS 4
- TRUST_ATTRIBUTE_FOREST_TRANSITIVE 8
Trust Type Values
|
Type
|
Corresponding Value
|
Explanation
|
|
1
|
TRUST_TYPE_DOWNLEVEL
|
The other domain is pre-Win2k (NTLM only supported)
|
|
2
|
TRUST_TYPE_UPLEVEL
|
The other domain is Win2k or later (Windows Kerberos
supported)
|
|
3
|
TRUST_TYPE_MIT
|
Other domain is actually an MIT Kerberos Realm (probably
UNIX)
|
|
4
|
TRUST_TYPE_DCE
|
The trusted domain is a DCE realm
|
Trust Direction Values
|
Direction
|
Value
|
|
Disabled
|
0x0
|
|
Inbound
|
0x1
|
|
Outbound
|
0x2
|
|
Bidirectional
|
0x3
|
SID Filtering
This field documents the status of SID filtering for the
trust relationship. SID filtering prevents DCs in one domain from making false
claims about a user’s membership in groups. For more information see https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc974396(v=ws.10).aspx.
Forest Trust Events
The Trust Information fields in events that involve
trusted forests are recorded in event IDs 4865 (Forest trust added), 4866
(Forest Trust Removed), and 4867 (Forest Trust Modified) and also require some
explanation. The example event ID 4866 shows an instance that
occurred upon a name-suffix routing change.
An explanation follows for elements in the Forest Trust Information
entry:
- Forest Root. The DNS name of the forest root domain of the
other forest in this trust relationship.
- Forest Root SID. The SID of the Forest Root: - usually
translated to the pre-Win2k domain name.
- Operation ID. The operation ID allows you to correlate all
the events that are part of this operation
- Entry Type. There are three possible entry types as shown in the table below.
- Flags. The Flags value seems to always be 0.
- Top Level Name. This domain is trusted or untrusted
(excluded); see Entry Types 0 and 1.
- DNS Name. See LSA_FOREST_TRUST_DOMAIN_INFO.
- Name. See LSA_FOREST_TRUST_DOMAIN_INFO.
- Domain SID. See LSA_FOREST_TRUST_DOMAIN_INFO.
|
Value
|
Entry Type
|
Comment
|
|
0
|
ForestTrustTopLevelName
|
This record identifies a domain (Top Level Name
below) of the trusted forest that this forest trusts.
|
|
1
|
ForestTrustTopLevelNameEx
|
This record identifies a domain (Top Level Name
below) of the trusted forest that this forest does not trust (excluded)
|
|
2
|
ForestTrustDomainInfo
|
This record contains an LSA_FOREST_TRUST_DOMAIN_INFO
structure which includes
Sid
DnsName
NetbiosName
|
Windows logs event ID 4713 when it detects a change to the domain's
Kerberos policy. Kerberos policy is defined in GPOs that are linked to the root
of the domain under Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security
Settings\Account Policy\Kerberos Policy.
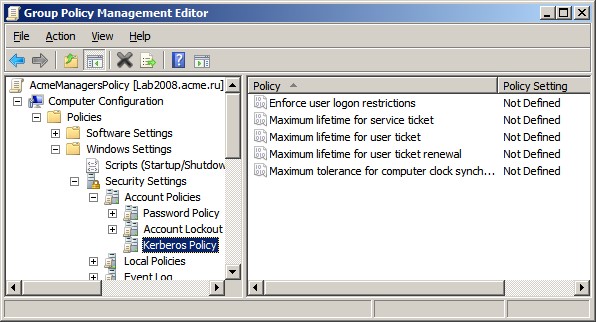
Unfortunately, the Subject fields in event ID 4713 don't
identify who actually changed the policy; Kerberos policy isn't directly
configured by administrators. Instead, Kerberos policy is edited in a GPO,
which then is applied to the computer. Therefore, this event always shows the
local computer as the entity that changed the policy (the computer is the
security principal under which gpupdate runs).
System Security Access Events
Some rights are extremely powerful, to the point of giving
the user administrator-equivalent authority. Event IDs 4717 and 4718 log
changes to 10 configurable logon rights such as
Access this computer from
the network
or Logon as a service. Other rights such
as Change the system time or
Take ownership of files and other
objects
are not granted. (These other rights fall under the Authorization
Policy Change subcategory.) The first column shows the name of each of the 10
logon rights as it appears on the Local Security Policy or Group Policy MMC.
The second column lists the actual system name of each right; this is the name
that appears in the event. A human can figure this difference out pretty
easily, but a computer program (such as an event filter) needs assistance. As
is often the case, Windows is inconsistent with wording. For example, “Access
this computer” really means “log on.”
|
Name in MMC
|
System Name
|
|
Access this computer from the network
|
SeNetworkLogonRight
|
|
Allow log on locally
|
SeInteractiveLogonRight
|
|
Allow log on through Terminal Services
|
SeRemoteInteractiveLogonRight
|
|
Deny access this computer from the network
|
SeDenyNetworkLogonRight
|
|
Deny log on as a batch job
|
SeDenyBatchLogonRight
|
|
Deny log on as a service
|
SeDenyServiceLogonRight
|
|
Deny log on locally
|
SeDenyInteractiveLogonRight
|
|
Deny log on through Terminal Services
|
SeDenyRemoteInteractiveLogonRight
|
|
Log on as a batch job
|
SeBatchLogonRight
|
|
Log on as a service
|
SeServiceLogonRight
|
Note that Deny rights are included. The description in
event ID 4718 (System security access was removed from an account) might seem to
indicate that a right was removed, but this interpretation is a little
misleading in the case of Deny logon rights. Someone might actually be granted
access when a Deny logon right is removed. If there is a conflict in which both
Deny and Allow rights are assigned, the Deny right takes precedence.
In Chapter 10, we talked about the use of rights and
privileges. The settings that were shown in Trust Direction values chart generate an event when
the policy is changed either through Group Policy or Local Security Settings.
These two events don’t tell you the real user who assigned or revoked the right
or rights; the Subject field always lists SYSTEM for the local computer.
Authorization Policy Change
When User Rights—that is, privileges other than logon
rights—are assigned, an event is generated in the Authorization Policy Change
subcategory.
|
Event ID
|
Title
|
|
4704
|
A user right was assigned.
|
|
4705
|
A user right was removed.
|
|
4714
|
Encrypted data recovery policy was changed.
|
Event ID 4704 occurs when a privilege (aka right) is
assigned; event ID 4705 occurs when a user privilege is revoked. Don’t confuse
event ID 4704 and event ID 4705 with the Privilege Use events described in
Chapter 10. Event ID 4704 and event ID 4705 log the assignment or revocation of
a user right, whereas Privilege Use events log the actual use of such rights.
These two Policy Change events log the user or group that
was the target of the change, as well as the system name of the right or rights
that were assigned or revoked. You can refer to the chart above in the System Security Access Events section to cross reference
a right’s system and friendly names. Like event ID 4717, these two events don’t
tell you the real user who assigned or revoked the right or rights; the Subject
field always lists SYSTEM for the local computer. As with logon rights, the
privilege name in the MMC differs from the system name of the privilege; the system name is the one that appears in the event.
|
Name in MMC
|
System Name
|
|
Adjust memory quotas for a process
|
SeIncreaseQuotaPrivilege
|
|
Add workstations to domain
|
SeMachineAccountPrivilege
|
|
Manage auditing and security log
|
SeSecurityPrivilege
|
|
Take ownership of files or other objects
|
SeTakeOwnershipPrivilege
|
|
Load and unload device drivers
|
SeLoadDriverPrivilege
|
|
Profile system performance
|
SeSystemProfilePrivilege
|
|
Change the system time
|
SeSystemtimePrivilege
|
|
Profile single process
|
SeProfileSingleProcessPrivilege
|
|
Increase scheduling priority
|
SeIncreaseBasePriorityPrivilege
|
|
Create a pagefile
|
SeCreatePagefilePrivilege
|
|
Back up files and directories
|
SeBackupPrivilege
|
|
Restore files and directories
|
SeRestorePrivilege
|
|
Shut down the system
|
SeShutdownPrivilege
|
|
Debug programs
|
SeDebugPrivilege
|
|
Modify firmware environment values
|
SeSystemEnvironmentPrivilege
|
|
Bypass traverse checking
|
SeChangeNotifyPrivilege
|
|
Force shutdown from a remote system
|
SeRemoteShutdownPrivilege
|
|
Remove computer from docking station
|
SeUndockPrivilege
|
|
Enable computer and user accounts to be trusted
|
SeDelegationPrivilege
|
|
Perform volume maintenance tasks
|
SeManageVolumePrivilege
|
|
Impersonate a client after authentication
|
SeImpersonatePrivilege
|
|
Create global objects
|
SeCreateGlobalPrivilege
|
|
Increase a process working set
|
SeIncreaseWorkingSetPrivilege
|
|
Change the time zone
|
SeTimeZonePrivilege
|
|
Create
symbolic links
|
SeCreateSymbolicLinkPrivilege
|
Event ID 4714 indicates that the specified computer's
Security Settings\Public Key Policies\Encrypting File System Data Recovery
Agent policy was modified. When an administrator modifies the data-recovery
policy for the Encrypting File System (EFS), Windows logs event
ID 4714 and specifies the old and new values for the policy. This event is
important because anyone who can edit a GPO can add himself or herself as a
data recovery agent to one or more computers, thereby accessing information
that has been encrypted by other users. Sometimes Windows logs event ID 4717
when nothing has changed, so examine the description of the event to determine
its relevance.
MPSSVC Rule Level Policy Change
Events in the chatty MPSSVC Rule Level Policy Change subcategory document the current configuration of the Windows Firewall (aka
MPSSVC) whenever it starts, as well as any changes to its configuration.
|
Event ID
|
Title
|
|
4944
|
The following policy was active when the Windows Firewall started.
|
|
4945
|
A rule was listed when the Windows Firewall started.
|
|
4946
|
A change has been made to Windows Firewall exception list. A rule was added.
|
|
4947
|
A change has been made to Windows Firewall exception list. A rule was modified.
|
|
4948
|
A change has been made to Windows Firewall exception list. A rule was deleted.
|
|
4949
|
Windows Firewall settings were restored to the default values.
|
|
4950
|
A Windows Firewall setting has changed.
|
|
4951
|
A rule has been ignored because its major version number was not recognized by Windows Firewall.
|
|
4952
|
Parts of a rule have been ignored because its minor version number was not recognized by Windows Firewall.
|
|
4954
|
Windows Firewall Group Policy settings has changed. The new settings have been applied.
|
|
4956
|
Windows Firewall has changed the active profile.
|
|
4957
|
Windows Firewall did not apply the following rule:
|
|
4958
|
Windows Firewall did not apply the following rule because the rule referred to items not configured on this computer:
|
Filtering Platform Policy Change
The events in the Filtering Platform Policy Change subcategory document the current configuration of the Windows Filtering
Platform (WFP) whenever it starts, as well as any changes to its configuration.
WFP is used by Windows Firewall and other software and can filter and modify
TCP/IP packets, monitor or authorize connections, filter Internet Protocol
security (IPsec)-protected traffic, and filter remote procedure calls (RPCs).
|
Event ID
|
Title
|
|
5440
|
The following callout was present when the Windows Filtering Platform Base Filtering Engine started.
|
|
5441
|
The following filter was present when the Windows Filtering Platform Base Filtering Engine started.
|
|
5442
|
The following provider was present when the Windows Filtering Platform Base Filtering Engine started.
|
|
5443
|
The following provider context was present when the Windows Filtering Platform Base Filtering Engine started.
|
|
5444
|
The following sub-layer was present when the Windows Filtering Platform Base Filtering Engine started.
|
|
5446
|
A Windows Filtering Platform callout has been changed.
|
|
5448
|
A Windows Filtering Platform provider has been changed.
|
|
5449
|
A Windows Filtering Platform provider context has been changed.
|
|
5450
|
A Windows Filtering Platform sub-layer has been changed.
|
Other Policy Change Events
The lone event in the Policy Change category
should have been in the Windows Filtering Platform subcategory.
|
Event ID
|
Title
|
|
5447
|
A Windows Filtering Platform filter has been changed.
|
Bottom Line
Policy Change events provide a few important
notifications, such as changes to audit policy, user right assignments, EFS
recovery policy, and trust relationships. Unfortunately, many of these events
only notify you of such changes; though they might specify the before and after
values for the changed settings, they don’t tell you who caused the change. To
track down the user behind the change, you’ll have to examine the Directory
Service events that we described in Chapter 9, to look for recent changes to
GPOs. The policies that relate to the Windows Firewall and Filtering Platform
will produce many events if these subcategories are enabled, so for most
environments, we recommend disabling them. Remember, you use Auditpol to
selectively disable the subcategories that you don’t need.