 Windows Security Log Event ID 4648
Windows Security Log Event ID 4648
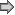
| Operating Systems |
Windows 2008 R2 and 7
Windows 2012 R2 and 8.1
Windows 2016 and 10
Windows Server 2019 and 2022
Windows Server 2025
|
Category
• Subcategory | Logon/Logoff
• Logon |
|
Type
|
Success
|
Corresponding events
in Windows
2003
and before |
552
|
4648: A logon was attempted using explicit credentials
On this page
This is a useful event for tracking several different situations:
- A user connects to a server or runs a program locally using alternate credentials. For instance a user maps a drive to a server but specifies a different user's credentials or opens a shortcut under RunAs by shift-control-right-clicking on the shortcut, selecting Run as..., and then filling in a different user's credentials in the dialog box that appears. Or a user logs on to a web site using new specific credentials. That is the case above in the example - Administrator was logged on to the local computer and then accessed a SharePoint server sp01.icemail.com as rsmith@mtg.com.
- This event is also logged when a process logs on as a different account such as when the Scheduled Tasks service starts a task as the specified user. Logged on user: specifies the original user account.
- With User Account Control enabled, an end user runs a program requiring admin authority. You will get this event where the process information is consent.exe. Unfortunately Subject does not identify the end user.
Unfortunately this event is also logged in situations where it doesn't seem necessary. For instance logging on interactively to a member server (Win2008 RC1) with a domain account produces an instance of this event in addition to 2 instances of 4624.
Free Security Log Resources by Randy
Subject:
This is the original account that started a process or connection using new credentials. In this case Administrator was logged on to the local computer.
- Logon ID is a semi-unique (unique between reboots) number that identifies the logon session just initiated. Any events logged subsequently during this logon session will report the same Logon ID through to the logoff event 4647 or 4634.
Account Whose Credentials Were Used:
These are the new credentials. In this case Administrator then logged on as rsmith@mtg.com.
Target Server:
This is the server (in this case a Sharepoint server) Administrator logged on to as rsmith@mtg.com. This section may be blank or indicate the local computer when starting another process on local computer.
Process Information:
This is the process that initiates the connection or new process. In this case it makes sense that it's Internet Explorer since we're accessing a Sharepoint site. The Process Name identifies the program executable that processed the logon. This is one of the trusted logon processes identified by 4611. Process ID is the process ID specified when the executable started as logged in 4688.
Network Information:
This is blank in many cases but in the case of Remote Desktop logons network address is filled in with the IP address of the client workstation. Source port, while filled in, is not useful since most protocol source ports are random.
Setup PowerShell Audit Log Forwarding in 4 Minutes
A logon was attempted using explicit credentials.
Subject:
Security ID: WIN-R9H529RIO4Y\Administrator
Account Name: Administrator
Account Domain: WIN-R9H529RIO4Y
Logon ID: 0x1ba0e
Logon GUID: {00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000}
Account Whose Credentials Were Used:
Account Name: rsmith@mtg.com
Account Domain: WIN-R9H529RIO4Y
Logon GUID: {00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000}
Target Server:
Target Server Name: sp01.IceMAIL.com
Additional Information: sp01.IceMAIL.com
Process Information:
Process ID: 0x77c
Process Name: C:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\iexplore.exe
Network Information:
Network Address: -
Port: -
This event is generated when a process attempts to log on an account by explicitly specifying that account’s credentials. This most commonly occurs in batch-type configurations such as scheduled tasks, or when using the RUNAS command.
Top 10 Windows Security Events to Monitor
Free Tool for Windows Event Collection